Randomized block design RB. In a randomized complete block design the experimenter constructs a blocks of b homogeneous subjects and uniformly randomly allocates the b treatments to everyone in each block.

Randomized Block Design With R Programming Geeksforgeeks
R-Codes for RCBD R is a free software environment for statistical computing and graphics.
. Randomized Block Design RBD or Randomized Complete Block Design is one part of the Anova types. In this type of design blocking is not a part of the algorithm. Design A randomized block design is a type of experiment where participants who share certain characteristics are grouped together to form blocks and then the treatment or intervention gets randomly assigned within each block.
It can be applied more than once but it is typically just applied once. The three basic principles of designing an experiment are replication blocking and randomization. RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGNS and LATIN SQUARES Jesús Piedrafita Arilla jesuspiedrafitauabcat.
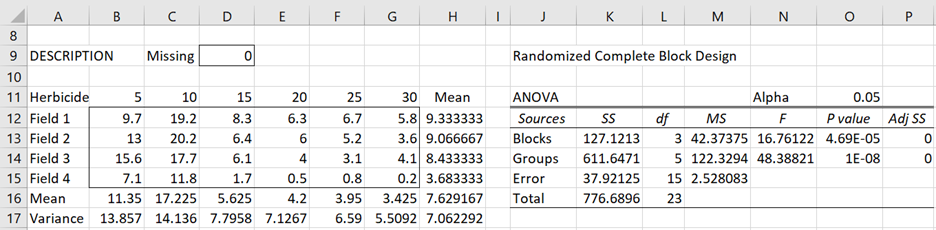
One of the important feature of R- software. RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN RCBD Description of the Design Probably the most used and useful of the experimental designs. An example with penicillin yield We illustrate this with an experiment to compare 4 processes A B C.
Within a block the order in which the four tips are tested is randomly determined. I am doing a pot experiment with 9 treatments 3 fertilizer and 3 pesticide treatments are combined and 6 replicates each therefore I have chosen 6 blocks. RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN WITH AND WITHOUT SUBSAMPLES The randomized complete block design RCBD is perhaps the most commonly encountered design that can be analyzed as a two-way AOV.
The goal is to control the e ects of a variable not of interest by bringing experimental units that are. 2 1 2 SSTotal y y n s Y As usual SSA Jy y2 k Compare row means exams SSB Ky y2 j Compare column means students SSE SSTotal SSA SSB. In that context location is also called the block factor.
Main Effects Interaction Effects Relative Efficiency Measures the ratio of the experimental error variance for the Completely Randomized Design sr2 to that for the Randomized Block Design sb2 Computed from the Mean Squares for Blocks and Error Represents how many observations would be needed per treatment in CRD to have comparable precision in estimating means. Im analyzing data collected from a Randomized Complete Block Design with missing observations so Im using Proc mixed SAS 94. Nevertheless I cannot manage to create it.
Ive found some answers in the pdf of the package named agricolae. I am trying to do a randomized complete block design with 3 re-arrangements in R. Try the different combinations of t k and r using lambda in your console and choose the answer which does NOT have a BIBD.
It then calculates lambda according to this formula. Randomized Block vs Completely Randomized designs Total number of experimental units same in both designs 28 leaves in total for domatia experiment Test of factor A treatments has fewer df in block design. As we can see from the equation the objective of blocking is to reduce the variability of the error.
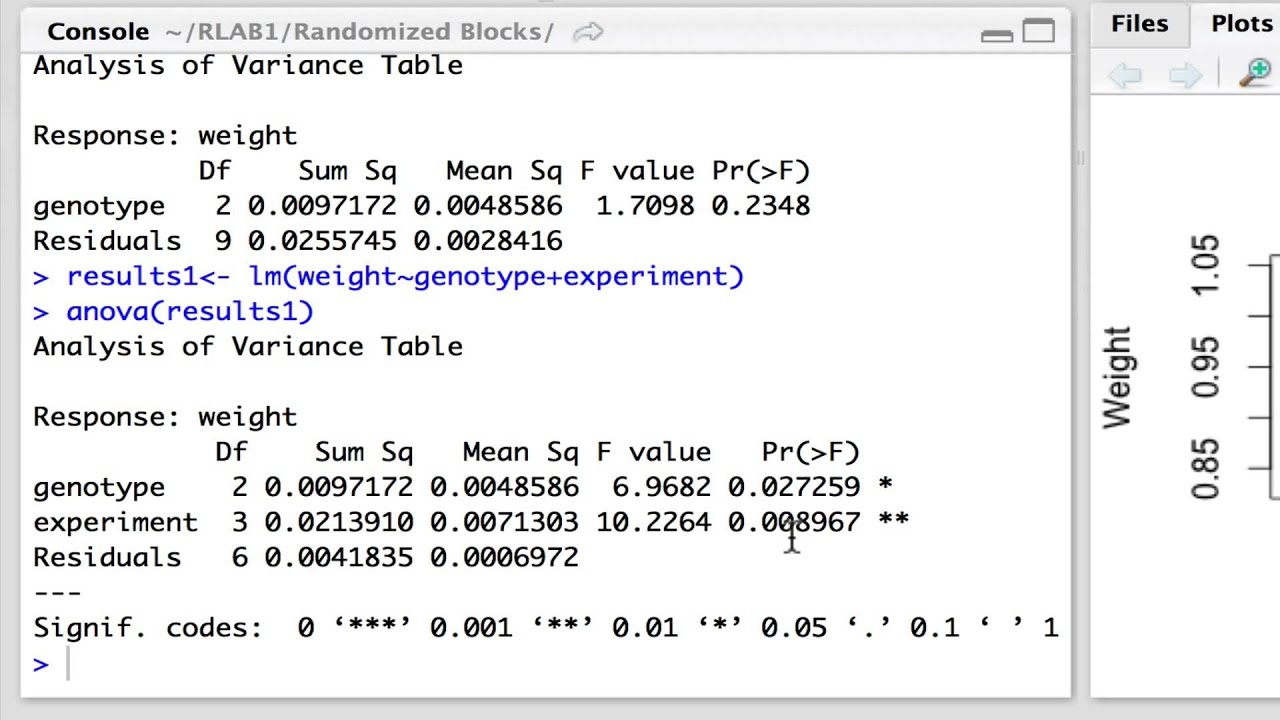
I have to implement a randomized complete block design and I would like to generate it with R. Within every block eg at each location the g treatments are randomized to the g experimental units eg plots of land. The treatments are assumed to act independent of the blocks and the overall error variability.
Does someone have an idea on how to do this please. The randomized complete block design is one of the most widely used designs. Within each block there is one fixed main plot factor A and one fixed subplot factor within each plot B.
This gives a randomized complete block design RCBD. The randomized complete block design RCBD uses a restricted randomization scheme. Within the block a treatment is allowed to occur once per arrangement and each individual pot is only allowed to occur once.
It compiles and runs on a wide variety of UNIX platforms Windows and MacOS. Items Randomized complete block design Concept of blocking Latin Squares design Basic commands lm 2. 3 RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN RCBD The experimenter is concerned with studying the e ects of a single factor on a response of interest.
Block Designs in R. This desin is called a randomized complete block design. I have 6 treatments and 4 blocks.
A complete description of R-software is given in Pinheiro and Bates 2007. Takes advantage of grouping similar experimental units into blocks or replicates. Randomized Complete Block Design.
The test data is. It takes as input t number of treatments k number of treatments per block and r number of repetitions. If it will control the variation in a particular experiment there is no need to use a more complex design.
We now consider a randomized complete block design RCBD. Sample the entire range of variation within the block. In such circumstances one can control for the day-to-day variation referred to as the block effects by ensuring that each of the levels of the other variables of interest occurs equally often on each manufacturing day ie equally often within each block.
The RCBD is the standard design for agricultural experiments where similar experimental units are grouped into blocks or replicates. A Randomized Complete Block Design RCBD is defined by an experiment whose treatment combinations are assigned randomly to the experimental units within a block. The blocks of experimental.
Reduced power of test RCB vs CR designs MS Residual smaller in block design if blocks explain some of variation in Y. A randomized complete block design RCBD usually has one treatment of each factor level applied to an EU in each block. Find the mean for each treatment row means each block column means and grand mean.
Generally blocks cannot be randomized as the blocks represent factors with restrictions in randomizations such as location place time gender ethnicity breeds etc. Variation in fertility or drainage differences in a field. Partition the SSTotal into three pieces.
Randomized complete block designs Say there are b treatments to be considered. The model takes the form. Here a block corresponds to a level in the nuisance factor.
Tread loss is measured in tread in mils 001 inches. Rk - 1 t - 1. Unbalanced and Repeated Measures.
Which is equivalent to the two-factor ANOVA model without replication where the B factor is the nuisance or blocking factor. In this design a set of experimental units is grouped blocked in a way that minimizes the variability among the units within groups blocks. Each block contains all the treatments.
It is used to control variation in an experiment by accounting for spatial effects in field or greenhouse. A design that would accomplish this requires the experimenter to test each tip once on each of four coupons. In this example you wish to compare the wear level of four different types of tires.
However variability from another factor that is not of interest is expected. A Randomized Complete Block Design. Randomized complete block designs differ from the completely randomized designs in.
Blocking increases the ability of the ANOVA tests to detect and.
Randomized Complete Block Designs Rcbd R

Randomized Complete Block Design Real Statistics Using Excel

Examples Using R Randomized Block Design R Bloggers

Chapter 5 Complete Block Designs Anova And Mixed Models

Randomized Block Designs In R Part 2 Practice Youtube
Randomized Block Designs In Rstudio Youtube


0 comments
Post a Comment